Deteriorated or “spalled” joints are the primary drawback in a concrete ground. Noticed lower contraction/management joints and development joints create interruptions within the concrete ground’s floor. These interruptions create influence factors alongside the joint edge and joints are then topic to deterioration or harm by the crossing wheels of fabric dealing with autos, pallet jacks, purchasing carts, and many others. Correctly filling and defending these joints with a semi-rigid epoxy or polyurea joint filler is one of the simplest ways to stop that joint deterioration.
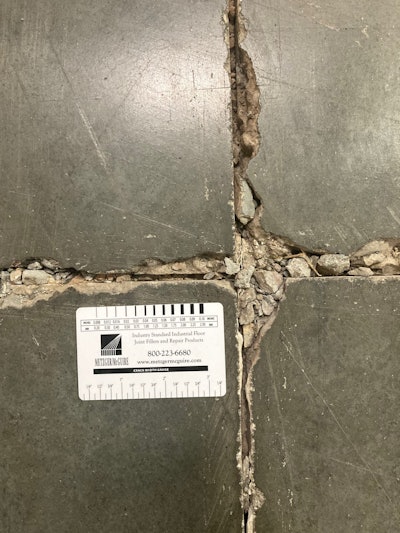 A deteriororated joint intersection. Metzger/McGuire
A deteriororated joint intersection. Metzger/McGuire
There are lots of potential causes of joint deterioration, the commonest of that are joints that have been by no means stuffed, joints crammed with a joint “sealant” or insufficiently inflexible joint filler, and joints being stuffed improperly. Extra causes can embrace joint filler separation or tearing, improper noticed reducing timing or the usage of warped or broken noticed blades on the newly positioned slab, poor ending alongside joint edges, slab edge curl or warping, and subgrade voids or deficiencies under the slab.
 Ravelled concrete joint edges from late sawcut timing. Metzger/McGuire
Ravelled concrete joint edges from late sawcut timing. Metzger/McGuire
The American Concrete Institute (ACI) of their studies 302 and 360 point out that to stop joint edge harm in trafficked flooring, joints must be crammed with a semi-rigid epoxy or polyurea joint filler having a Shore A hardness of A80 or greater per ASTM D 2240. This customary dates again to the early 1980’s, and present draft revisions of those paperwork revise this advice to an elevated filler hardness of A85+.
 A cross part of a structural restore the place the noticed lower was not deep sufficient. Metzger/McGuire
A cross part of a structural restore the place the noticed lower was not deep sufficient. Metzger/McGuire
A common rule of thumb is that the Shore A hardness of the joint filler must be equal to or larger than the Shore A hardness of the wheels crossing the joints. If a semi-rigid filler will not be sufficiently inflexible, it may well deflect underneath a crossing load, exposing the joint edges to influence harm.
Use this desk to assist match the joint width and constructing to Shore A hardness.
| Joint Restore Width | Facility Sort | Restore Product | Shore A Hardness (Minimal) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/4 to 1/2 in. | Heavy Responsibility Industrial Warehouse, Distribution Heart | Semi-Inflexible Polyurea Joint Filler | A85+ |
| Semi-Inflexible Epoxy Joint Filler | A85+ | ||
| 1/2 to 1 in. | Semi-Inflexible Polyurea Joint Filler | A90+ | |
| Semi-Inflexible Epoxy Joint Filler | A90+ | ||
| 1 to 4 in. | Sand Modified Semi-Inflexible Epoxy Joint Filler | A98+ (with sand mixture) | |
| Structural Epoxy, or Urethane/Polyurea Mortar | |||
| 1/4 to 1/2 in. | Reasonable Responsibility Industrial Warehouse, Distribution Heart | Semi-Inflexible Polyurea Joint Filler | A80+ |
| Manufacturing | Semi-Inflexible Epoxy Joint Filler | A80+ | |
| 1/2 to 1 in. | Reasonable Responsibility Industrial Warehouse, Distribution Heart | Semi-Inflexible Polyurea Joint Filler | A85+ |
| Manufacturing | Semi-Inflexible Epoxy Joint Filler | A85+ | |
| 1 to 4 in. | Reasonable Responsibility Industrial Warehouse, Distribution Heart | Sand Modified Semi-Inflexible Epoxy Joint Filler | A98+ (with sand mixture) |
| Manufacturing | Structural Epoxy, or Urethane/Polyurea Mortar | ||
| 1/4 to 1/2 in. | Retail, Grocery Restaurant, College | Semi-Inflexible Polyurea Joint Filler | A80+ |
| Semi-Inflexible Epoxy Joint Filler | A80+ | ||
| 1/2 to 1 in. | Semi-Inflexible Polyurea Joint Filler | A80+ | |
| Semi-Inflexible Epoxy Joint Filler | A80+ | ||
| 1 to 4 in. | Sand Modified Semi-Inflexible Epoxy Joint Filler | A98+ (with sand mixture) | |
| Structural Epoxy, or Urethane/Polyurea Mortar | n/a |
Underlying Causes
 Measuring slab deflection. Metzger/McGuire
Measuring slab deflection. Metzger/McGuire
One widespread situation is subgrade voids resulting in slab panel deflection or “rocking.” If slab panels deflect or drop as autos cross the joint, the joint edge on the upper aspect can endure dramatic influence harm. ACI 360 notes that slab deflection of greater than .060” (1.5 mm) will result in lowered service lifetime of the ground and will probably be repaired.
 In the course of the set up to stabilize a slab utilizing structural foam.Metzger/McGuire
In the course of the set up to stabilize a slab utilizing structural foam.Metzger/McGuire
 After, a stabilized slab with joints repaired.Metzger/McGuire
After, a stabilized slab with joints repaired.Metzger/McGuire
Operational circumstances reminiscent of dragging or pushing pallets might require behavioral adjustments to keep away from future joint harm. Seasonal motion of joints also needs to be thought-about earlier than tackling repairs, particularly in buildings with no energetic local weather management or in flooring with prolonged or restricted joint ground techniques.
The less joints the ground has, the extra dramatic the motion that takes place at every location, and the extra delicate the popular timing of restore. The place continuous joint motion is set to be the reason for joint failure, repairs ought to optimally be carried out halfway via humidity and temperature cycles, sometimes spring or fall.