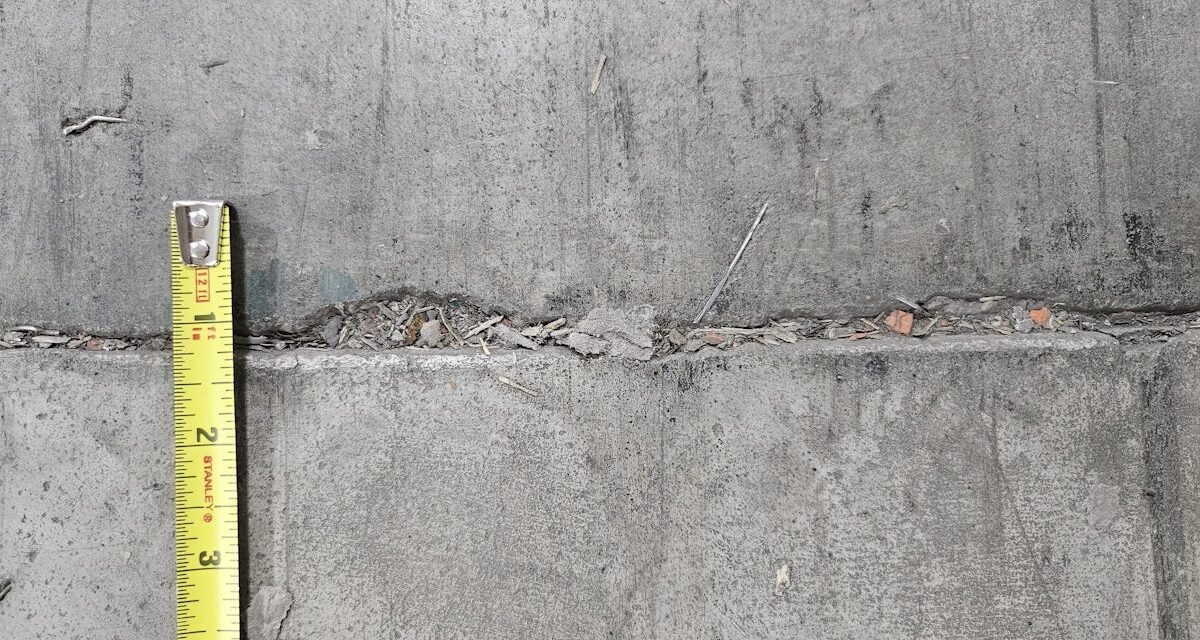
Jointed warehouse flooring sometimes require repairs throughout their service life. Some flooring require extra repairs than others, relying on the design, development, and publicity circumstances, particularly flooring uncovered to small-wheeled forklift visitors. Joint edges of each contraction and development joints spall (break off) when both the joint filler is not defending the perimeters from wheel affect, or joints are unstable inflicting differential deflections between the adjoining slab panels. When wheeled visitors crosses unstable joints, differential slab defections expose joint edges to wheel impacts creating edge injury. Edge injury can improve till joint widths and injury depths intrude with wheeled visitors and clean operations of the ability.
Under are varied restore choices for spalled and unstable joints. Previous to performing spall repairs, joints must be checked to make sure stability; in any other case, edge repairs won’t final. Joint edge repairs are categorized by the extent or primarily the width of the sting spall injury: Minor, Medium, and Extreme.
Minor Edge Spalling
Minor edge chips and spalls can merely be repaired by eradicating the present joint filler and refilling the joint reservoir with new joint filler (semi-rigid epoxy or polyurea) permitting the filler materials to circulation into the sting chips and small spalls. If wanted, a thicker sawblade can be utilized to extend the width of the joint reservoir to both take away or scale back the dimensions of chips and spalls. After eradicating the filler or widening the joint, completely clear the brand new joint reservoir. Barely overfill the joint with the brand new filler and after the suitable treatment time, shave or grind the filler flush with the ground floor. Make certain the brand new joint filler was designed to fill and defend joints in industrial flooring with a minimal Shore A hardness of 80. Shore hardness pertains to the stiffness of the filler. Adequate stiffness is required to help and defend joint edges from chipping and spalling.
Medium Edge Spalling
Medium edge spalling (as much as roughly 1 in.) requires the width of the joint reservoir to be sufficiently enlarged to take away the sting spalls. Use particular joint widening blades or a number of blades with or with out spacers to enlarge the width of the joint reservoir to chop away the sting spalls and kind a brand new “T” formed reservoir. When utilizing a number of blades, the middle blade ought to minimize to the depth of the unique joint. For outer blades, the depth of the sawcuts must be about 1/2 in. to three/4 in. Depth of the joint must be the unique joint depth or a minimal of two in. for a thru-slab joint (i.e., development joint).
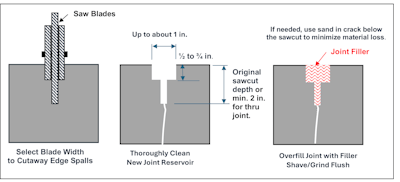
Subsequent, completely clear the newly shaped reservoir and barely overfill with joint filler. After the suitable treatment time, shave or grind flush with the floor of the ground. Make certain the brand new joint filler is suitable for the full width of the brand new joint reservoir. Producers normally present instructions for including dry silica sand to change normal semi-rigid fillers to accommodate wider joints. It’s vital the restore is flush with the floor of the ground so wheeled visitors travels easily over the restore.
Extreme Edge Spalling
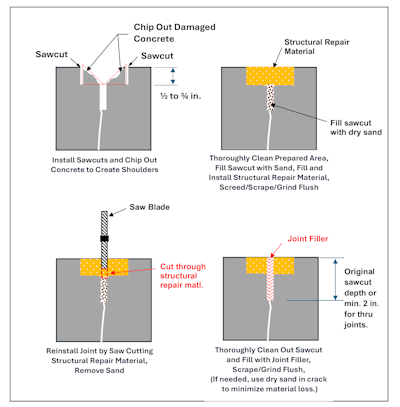
For extreme edge spalls with joint widths exceeding 1 in., measure and uniformly sawcut parallel alongside the joint to embody edge spalls. Sawcut depth must be about 1/2 to three/4 in. as illustrated under to create joint shoulders. Subsequent, chisel out the broken concrete between sawcuts utilizing a lightweight chipping hammer creating joint shoulders. Totally clear out the brand new joint reservoir and fill the sawcut under the shoulders with dry silica sand and barely overfill the reservoir with a structural restore materials designed for rebuilding joint shoulders in industrial flooring.
After curing, grind the structural restore materials flush with the floor and reinstall the sawcut fully by way of the structural restore materials. Restoring the sawcut permits the joint to open/shut minimizing the chance of future slab cracking. Depth of the joint must be equal to the unique sawcut depth or not less than 2 in. for thru-slab joints. Clear out the sawcut, take away the sand, and barely overfill the joint with a semi-rigid joint filler. After the suitable treatment interval, shave or grind the joint filler flush with the floor of the slab.
Producers of joint restore merchandise have different supplies, suggestions, and strategies to restore minor to extreme joint edge spalling. You should definitely learn the instructions, particularly, methods to put together the joint reservoir and observe the producers’ directions. If questions come up, get assist by contacting a technical consultant for the product.
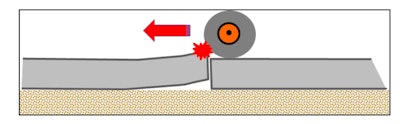
 Differential joint deflections could be measured utilizing a flooring profiler as a shifting forklift passes over the joint. KB Engineering LLC
Differential joint deflections could be measured utilizing a flooring profiler as a shifting forklift passes over the joint. KB Engineering LLC
Repairing Unstable Joints
Slab curling is a typical phenomenon for slabs as a consequence of a differential moisture gradient between the highest and backside of the slab leading to differential concrete shrinkage. Differential prime and backside concrete shrinkage trigger slabs alongside joints to curve upwards leaving a void house beneath the slab. Like inserting a sheet of plywood on the bottom and exposing the highest facet to the solar; edges curl upwards. When forklifts cross curled joints, differential deflections of the adjoining panels expose the main joint edge to wheel impacts. Unstable joints must be stabilized earlier than repairing edge spalls; in any other case, the restore will fail prematurely as a result of continued wheel impacts.
Proof of unstable joints are joint edge injury, joint clicking or banging as forklifts cross joints, scrapes and black tire marks alongside the curled portion of the panels. Additionally, “sounding” the slab with a heavy hammer can establish the extent of the sting and nook curl by revealing the portion of the slab that has lifted off the bottom. Sometimes, the curled portion will lengthen 1 to 2 ft perpendicular from the joint. Sounding consists of hanging the concrete with a heavy hammer (e.g., 3 lb) and listening to the ensuing sound. A hole sound signifies the slab has curled or lifted off the bottom.
Filling the voids beneath curled slabs alongside joints after which grinding joints flat to take away bumps related to the curling is the perfect restore choice. After stabilizing joints, restore edge chipping and spalling utilizing one of many strategies described above.
Joint stabilization begins with sounding panels to estimate the extent of the slab curling. Subsequent, set up a gap drill sample based mostly on the void areas and the producer’s suggestions for the fabric and tools getting used. Then, fill the cavities beneath the slab alongside the joint by injecting an increasing polyurethane foam or pump a flowable mortar by way of drilled holes alongside the joint. After curing, the restore supplies will harden and help the slab to get rid of slab deflections.
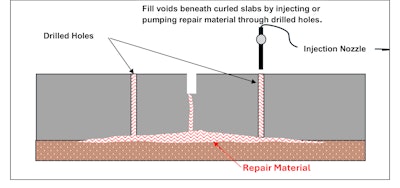
After filling the voids beneath the slab, restore the drill holes utilizing a product particularly designed to restore holes in industrial flooring. Then grind the joint flat and if wanted, restore the joint utilizing one of many spall restore strategies described above and refill the joint reservoir. Stabilizing joints will assist forestall continued joint edge deterioration and lengthen the service lifetime of joints, particularly edge repairs.
For unprotected and/or unstable joints, the speed of edge injury will increase with publicity, particularly when uncovered to wheeled visitors with small, onerous wheels. Due to this fact, performing repairs sooner reasonably than later will assist reduce the extent and price of joint spall repairs.